All CBD extracts must be tested for their potency to ensure correct labelling and to ensure that the THC content is below the legal limit. This will usually be expressed as a percentage or as total mg of CBD per bottle.
There are several scientific techniques that can be employed to measure THC and CBD concentrations. The most used techniques are Liquid Chromatography (LC-UV/Vis abbreviated to just LC) or Liquid Chromatography with Mass Spectrometer detection (LC-MS). LC or LC-MS are employed to separate and quantify each chemical in a liquid solution.
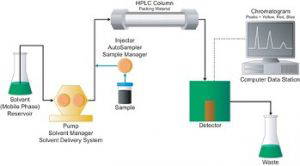
To use LC to separate and detect CBD and THC content of a plant extract, or an oil, the sample is collected and dissolved in a solvent such as Ethanol or Isopropanol. The solution is then injected onto the HPLC column, where it is pumped at high pressure through the column with a mobile phase. The column contains materials (stationary phase) that are utilised to separate the molecules within the sample via their interactions between the mobile phase and the stationary phase. The surface interaction can be manipulated to preferentially separate molecules with different chemical properties. A detector lies at the end of the column which enables quantification of each separated molecule.
As mentioned, LC can be coupled with a UV detector, usually measuring UV light absorbance or, more specific to the technique employed by Target Labs for CBD analysis, a Mass Spectrometer. Each molecule has a specific mass that the Mass Spectrometer is programmed to detect. To further enhance this detection the Mass Spectrometer can fragment molecules that produces specific fragments that are also detected as part of a mass transition. This use of mass transitions produces much more selective detection which enhances accuracy and precision of the analysis. In relation to the different types of cannabinoids, these will first be separated on the HPLC column, eluting from the column at different times depending on their interaction with the mobile and stationary phases. They will then pass into the mass spectrometer where mass separation and detection will occur allowing for full characterisation of the sample analysed. Quantitation of unknown samples is facilitated by analysis with calibration standards and QCs of known concentrations.
Figure 1 – An overview of the HPLC process (source: https://www.waters.com/)
Whilst there is currently no standard protocol established for testing across the country, any reputable laboratory can be relied upon to produce an accurate and reliable report in the form of a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). All CBD products should be tested by a reliable 3rd party testing lab, which will use relied methods such as the above.